This case study explores how Tonxing Molds from Jingdezhen uses 3D scanning for porcelain molds production.
Table of Contents
Project Background
This case study takes place in Jingdezhen, a city famous for its fine porcelain. In fact, Jingdezhen is often called the “Porcelain City”, having been producing traditional Chinese porcelain for over 1,000 years.
Today, we’re sharing the story of Tongxing Mold, a company that has been manufacturing porcelain molds since 2017. The Tongxing Mold team recently adopted 3D scanning technology to enhance its porcelain mold quality and process.
This case study is also available in video format:
Challenges of Traditional Porcelain Mold Design and Production
The traditional porcelain manufacturing process involves several challenges. Let’s take a look at these porcelain mold challenges before explaining how 3D scanning can help.
Limitations of 2D Drawings
Designing porcelain objects often requires multiple back-and-forths between multiple parties. Usually, the design team or client provides 2D drawings. While some 3D effect can be imagined with 2D drawings, there can easily be a large gap between the sketch (and the customer’s expectations) and the final product.
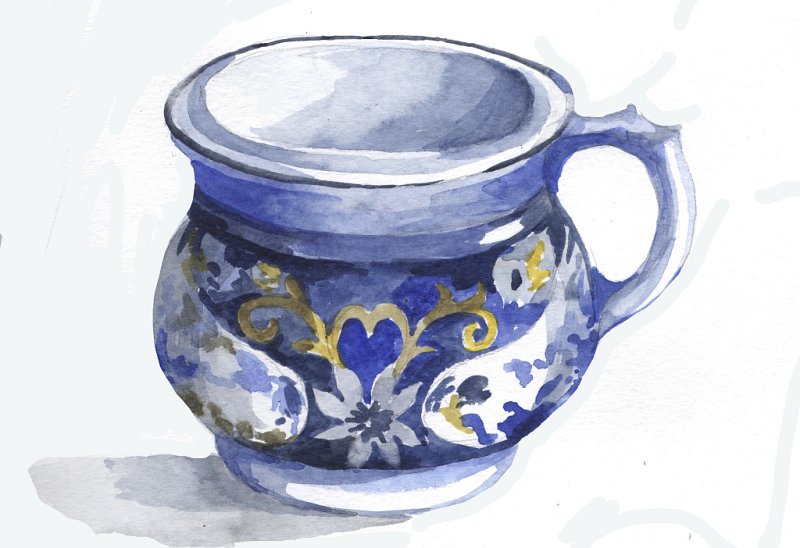

Measurement error
Porcelain manufacturing requires multiple precision measurements, especially when converting 2D drawings to 3D models. The designer’s level of experience, production materials, and environment are all factors that may influence measurement accuracy. When the measurements are incorrect, it can lead to reworking the mold.
Time-consuming and Costly Reworking
In the traditional approach, reworking is typical. That’s because the design or appearance is not truly final until after the porcelains have been fired and molded. It costs time and money to re-optimize the design and manufacture it.

How 3D Scanning Technology Can Optimize Porcelain Mold Design and Production
3D scanning can simplify the porcelain manufacturing process in several ways. Let’s take a look at the different steps involved – from 3D scanning clay molds to manufacturing the final object – to understand how.
3D Scanning the Clay Molds
Tongxing Mold chose to adopt the EinScan Pro HD 3D scanner. It’s a versatile, multifunctional device offering three scanning modes:
- handheld rapid mode
- handheld HD mode
- fixed mode with/without turntable
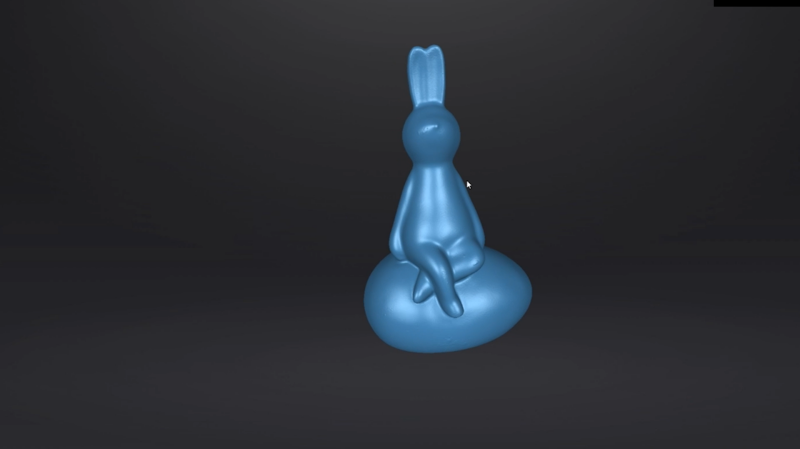
Smaller clay molds can be scanned fully automatically using a turntable. The scanning time for a single frame in fixed mode with a turntable is less than 0.5 seconds.
In the case of the rabbit mold below, the complete 360-degree scan took under 3 minutes. Tongxing Mold obtained high-precision 3D data with a point distance of just 0.24mm. The latter resolution enables a rich, highly detailed display of the 3D model. This lays a solid data foundation for the subsequent production of porcelain products.


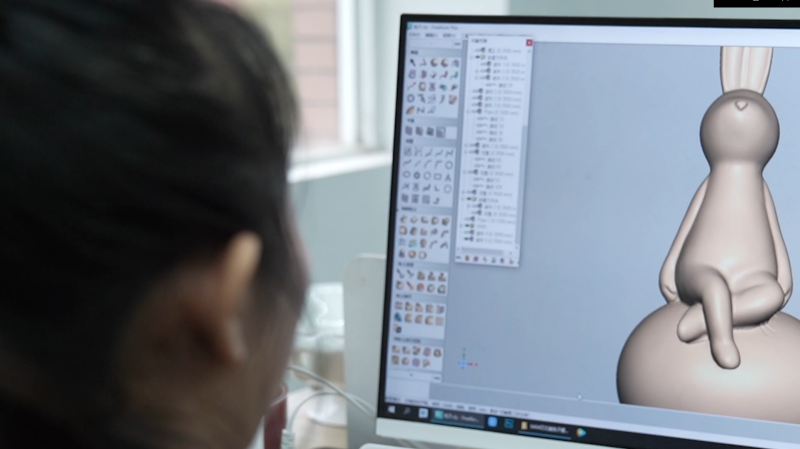
Designing the Porcelain Mold in 3D
The 3D scanned data can then be imported into professional 3D design software such as Geomagic Freeform. Tongxing Mold’s team uses this software to modify the model’s shape and size. They can view the 3D model from multiple angles and enlarge or downsize it. This makes it easier for designers to easily communicate about detail adjustments.

Producing the Master Form By 3D printer/CNC machine
The next step is to import the final 3D model into the 3D printer/CNC machine to generate the porcelain master form. A porcelain master form is a physical product model that is created with a 3D printer or CNC finishing machine from a digital 3D model.
Using 3D printing or CNC technology to make the porcelain master form has significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of the porcelain manufacturing process. It eliminates the need for manual labor and minimizes the risk of errors in traditional manufacturing methods.
Produce the master form using the 3D printer/CNC machine
Mass Production
The printed porcelain master form can visually present the design effect. After the demand is communicated without error, the production mold can be turned by plaster and put into the production line. The finished porcelains are subsequently manufactured through multiple processes such as water refilling, glazing, and firing.
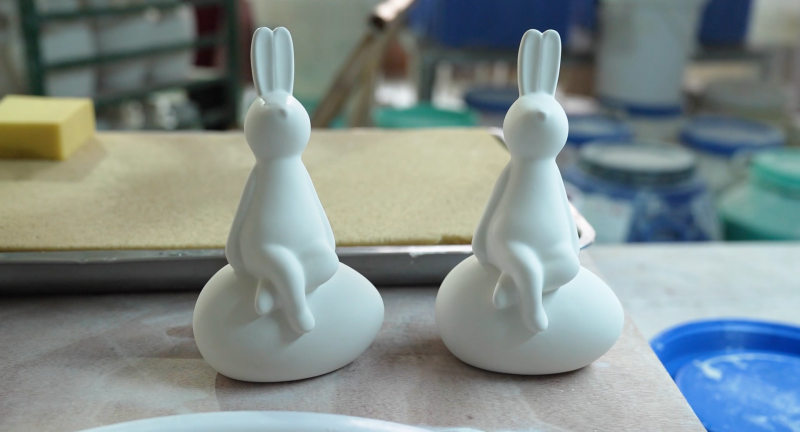
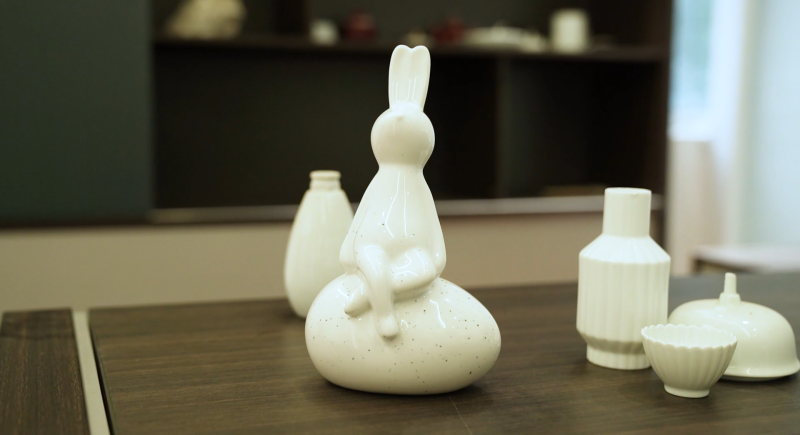


Conclusion
By adopting 3D scanning technology in their porcelain manufacturing process, Tongxing Mold has revolutionized the traditional approach. With 3D scanning technology, Tongxing Mold can create high-precision 3D data of clay molds, easily modify designs using 3D design softwares, and manufacture master models and final products using 3D printers/CNC machines with minimal waste.





