Those who have been acquainted with EinScan-Series 3D scanners know that in the turntable scanning mode, except for Einscan-SE, every device has 3-4 kinds of align modes to choose from. But what´s the basis of choice for each these modes?
In this blog post, we will introduce the differences between the align modes of the turntable scanning mode in detail.
Note: the choice of align mode is not limited to one, there is an overlap between different align modes, which means that there are certain objects that can be compatible with different align modes. Therefore the categorization of the align modes does not depend on objects.
This article will try to explain the best align mode for specific scanning situations.
The alignment in turntable mode refers to the alignment of scan data after one full turn of 360 degrees. When continuing to scan, the align method between the data acquired by the current scan and from the previous scan is based mainly on features. If enough markers have applied to the object, and marker alignment has been chosen for both scans, the data from both scans will be aligned based on the applied marker points.
Table of Contents
Feature Alignment:
Generally speaking, feature is the geometric shape of an object. Feature Alignment is the alignment of data from multiple scans according to the object’s collective shape. Therefore, in this align mode, objects need to have distinguished features in order to be aligned correctly. This align mode is mainly for objects rich in features.
 Object with rich features Object with fewer features
Object with rich features Object with fewer features
Note:
- If the object is too small, it is possible that the features can’t be recognized by the software.
- Lots of repeated patterns are not regarded as rich in features. As in the picture below, the object has a lot of repeated structures, therefore it doesn’t have rich features.
Turntable Marker Alignment:
The turntable marker points are the white points on the turntable. This align mode, as the name implies, works by placing the object to be scanned on the turntable and the alignment of the data depends on the recognition of the marker points as the turntable rotates. Therefore, to ensure that enough marker points are recognized in the scan, the angle of the scanning head needs to be adjusted, so that the marker points can be scanned. The object to be scanned also must not be so large as to conceal too many of these points.

Marker Alignment:
Marker alignment requires a certain density of marker points to be pasted on the surface of the object in advance, and during the scanning process, the data is aligned according to these markers. This align mode is mainly used for objects with a lack of features. Without markers, the alignment of these object scans might poise errors.
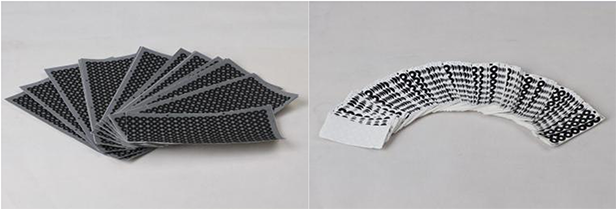
Note: Selecting this mode requires covering the coding points on the turntable.
Turntable Alignment:
Turntable alignment is to use the positional relationship between the turntable axis and the scanning head determined during the calibration of the device. In this align mode, no relative position movement between the scanning head and the turntable is allowed after the calibration is completed; and if a relative position movement occurs, it is necessary to recalibrate.
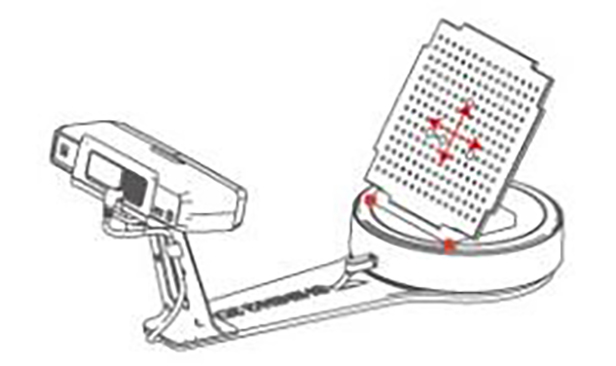
The following explanation is based on examples of objects.
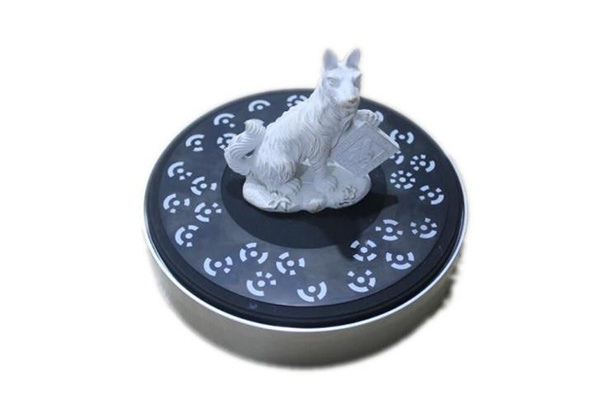

If the object has rich features and does not conceal too many coding points, so it is possible to select turntable alignment, turntable coded alignment, or feature alignment to obtain complete object data within 2-3 scans.
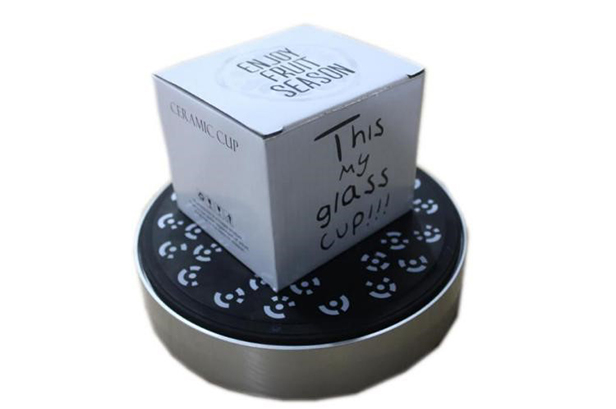

Objects with insufficient features, for a single scan turntable alignment or turntable marker alignment, can be selected. In order to complete the scan of the box, at least two scans are needed. Therefore marker alignment may be more adequate.
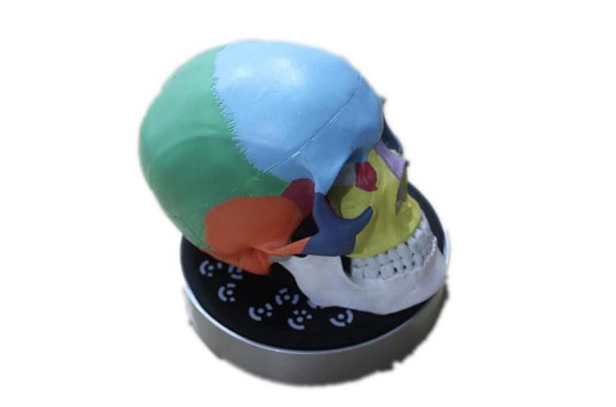

In this case, the object conceals most of the turntable marker points, but it has sufficient features, so turntable alignment or feature alignment can be selected to complete the scanning of data.
In order to cope with the scanning of various shapes and objects, EinScan 3D scanners provide a wide range of align modes that may cause confusion to new users, but we hope that this article helps you to determine the best align mode for the objects you need to scan.






